Society: AGA
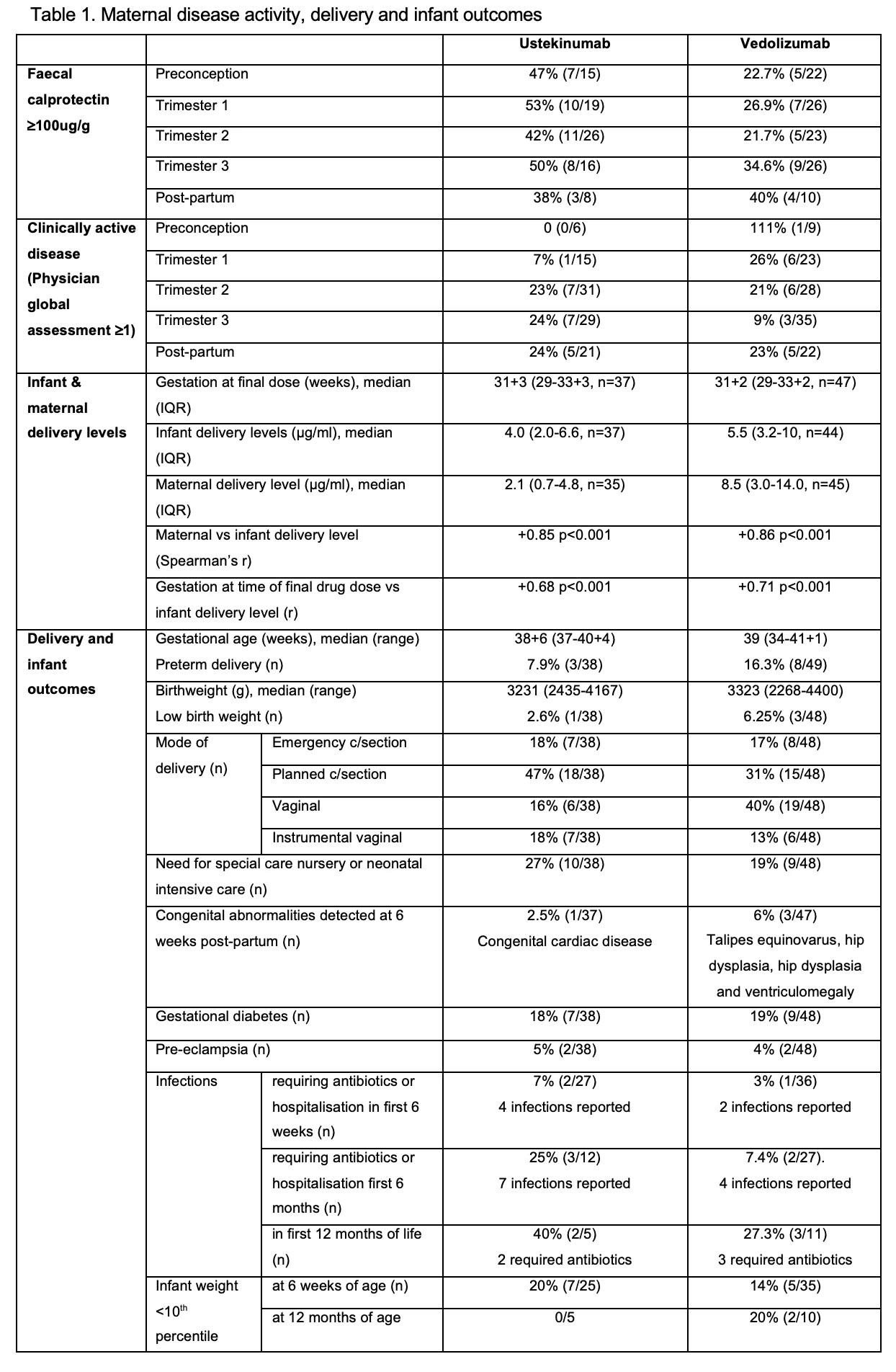
Background: The impact of pregnancy on vedolizumab (VDZ) and ustekinumab (UST) pharmacokinetics is not well defined. Similarly, the time to infant clearance and outcomes following in-utero exposure require elucidation. We aim to define the stability of UST and VDZ levels in pregnancy, placental drug transfer, and the time to and factors influencing infant drug clearance.
Methods: This multicentre prospective cohort study recruited women with IBD who were pregnant or planning pregnancy and receiving VDZ or UST. Trough drug levels, and clinical and biochemical data were documented pre-conception and in each trimester (T) of pregnancy. Maternal and infant drug levels were obtained at delivery and repeated in infants until clearance was acheived. Infant outcomes were assessed to 2 years of age. Drug levels were measured by ELISA (Theradiag) with a lower limit of detection of 0.25 mg/mL (VDZ) and 0.4 mg/mL (UST).
Results: 97 women aged median 31 (IQR 29-34) y with 54 receiving VDZ (41,17 with Crohn’s disease respectively) were included. Clinical and biochemical disease remission was maintained in the majority (Table 1). Median VDZ levels decreased by 42% from T1 to T3 (p<0.001; Skilling’s Mack) without a corresponding increase in median faecal calprotectin (T1 21.5ug/g (14-110) vs T3 59 (17-131) p=0.65; Wilcoxon signed-rank). UST levels were stable over the course of pregnancy (p=0.14) (Fig 1). 82% (VDZ) and 78% (UST) of participants continued drug into T3. Favourable delivery and infant outcomes, comparable to previously reported cohorts, were observed (Table 1). Infant:maternal drug level ratio was 1.74 (1.24-3.5, n=35) for UST and 0.71 (0.52-0.91, n=44) for VDZ. Delivery levels in infants correlated positively with concomitant maternal levels and gestation at time of final drug dose (Table 1). 67% UST and 90% VDZ exposed infants cleared drug by 15 weeks (p=0.06; two sided test of proportions), with a time to clearance of 13 (9-22) weeks for UST and 11 (8-13) weeks for VDZ (p=0.11; non-parametric comparison of medians). Time to clearance correlated positively with infant delivery level (Table 1). There was no difference in the time to infant clearance between those receiving their last dose in T2 vs T3 (UST p=0.45 or VDZ p=0.44)
Conclusion: UST levels are stable over the course of pregnancy. VDZ levels fall but without a parallel increase biochemical disease activity. Proactive dose adjustment and level monitoring during pregnancy is therefore not necessary. Differences in placental transfer of UST and VDZ were confirmed, with the infant:maternal drug level ratio at delivery lower for VDZ than UST. Both are cleared prior to 15 weeks in the majority of infants, but the higher placental transfer of UST results in numerically fewer exposed infants clearing by this timepoint. No concerning infant outcomes were identified in this cohort.
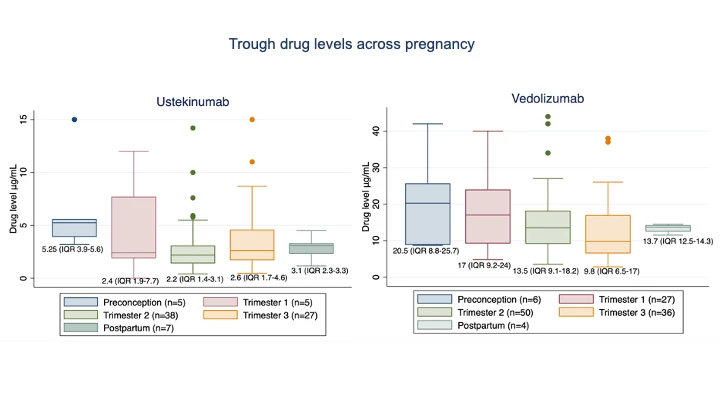
Trough drug levels across pregnancy
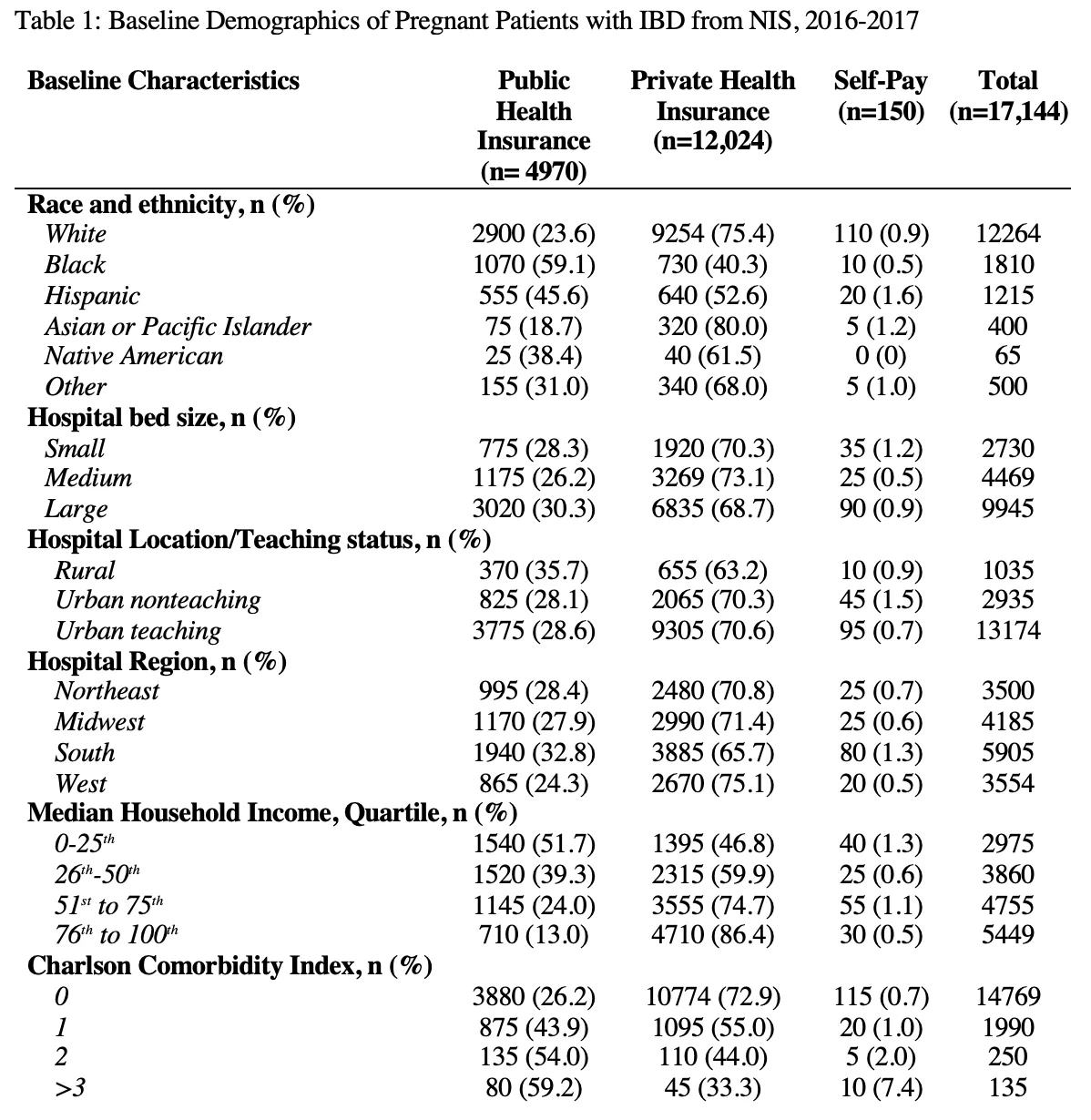
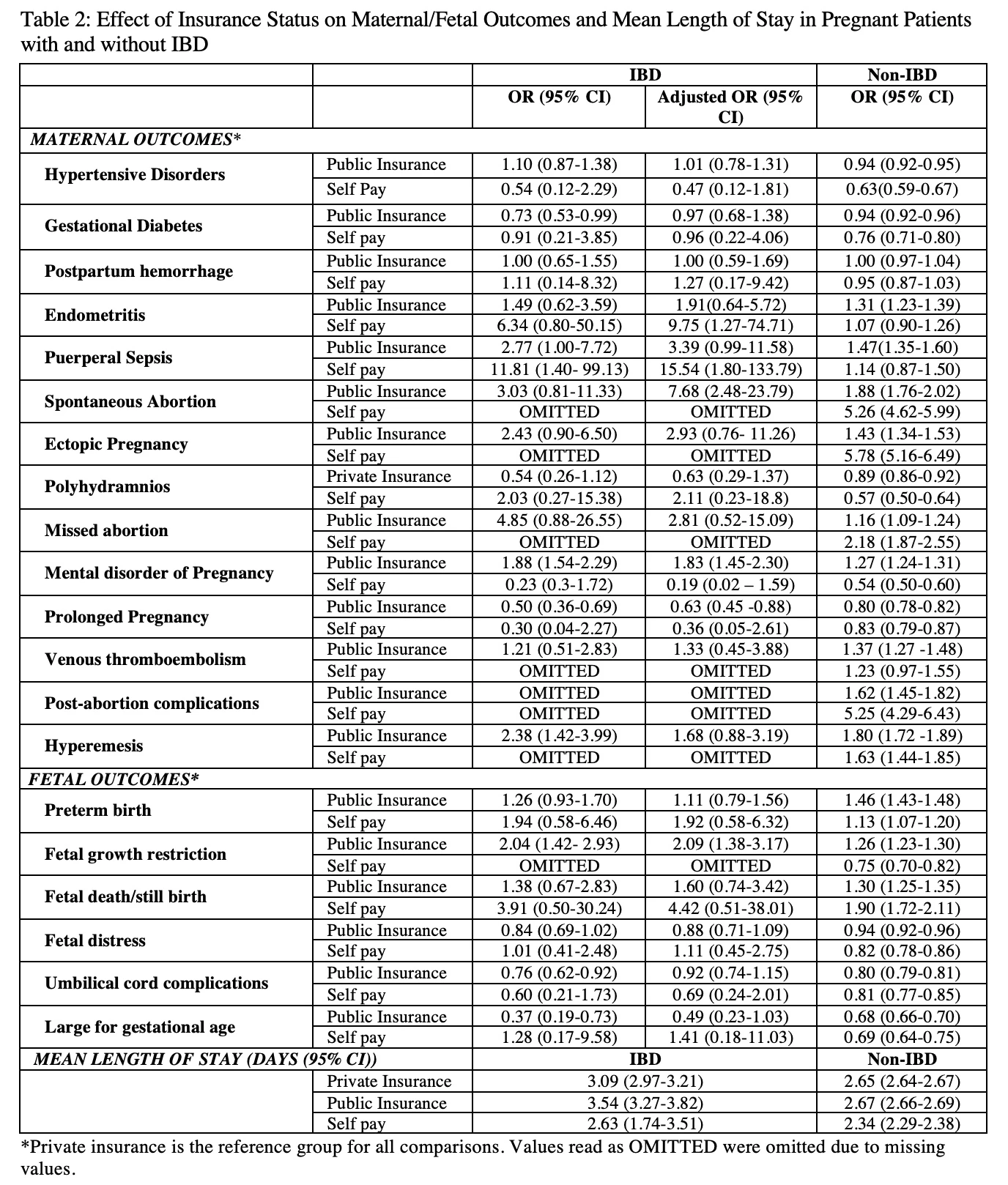
Introduction: The peak age of onset for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) overlaps with women’s reproductive age. There has also been an increase in IBD in the pregnant population in recent years. Studies suggest women with IBD may have worse maternal and fetal outcomes and increased hospital resource utilization during pregnancy. We hypothesize that insurance status as a social determinant of health (SDOH) may play a role in these outcomes.
Methods: The National Inpatient Sample (NIS) from 2016-2017 was analyzed to identify all pregnant women and stratified by IBD diagnosis based on ICD 10 codes. Maternal outcomes of interest were hypertensive disorders, gestational diabetes, post-partum hemorrhage, venous thromboembolism, postpartum endometritis, spontaneous abortion, missed abortion, post-abortion complications, ectopic pregnancy, polyhydramnios, hyperemesis, mental disorder during pregnancy, prolonged pregnancy, and length of stay. Fetal outcomes of interest were preterm delivery, fetal growth restriction, fetal death, fetal distress, cord complications and large for gestational age. Univariate analyses were conducted to determine the effect of insurance status (public, private, self-pay) on maternal and fetal outcomes. Outcomes were adjusted for age, race, hospital bed size, location/teaching status of hospital, hospital region, median household income, and Charlson Comorbidity index.
Results:
There was a total of 17,144 records for hospitalized pregnant women with IBD, of which 4,970 had public health insurance, 12,024 had private health insurance and 150 were self-pay (Table 1). After adjusting for potential confounders, pregnant women with IBD with public health insurance had increased odds of hospitalization for pregnancy-related mental disorders, hyperemesis, fetal growth restriction, and spontaneous abortion and lower odds of hospitalization for prolonged pregnancy than those with private insurance. The mean length of stay (LOS) for pregnant IBD patients was higher than those without IBD. Patients with public insurance had a higher mean LOS than other insurance types regardless of IBD status (Table 2).
Conclusion: NIS data suggest an association with increased adverse maternal/fetal outcomes for pregnant IBD patients with public compared to private health insurance. While public health insurance appears to have a protective factor for prolonged pregnancy, the increased odds of the other adverse outcomes described are likely of higher threat to maternal and fetal health. Other SDOH factors may also have a role in these outcomes among pregnant women with IBD and further studies are warranted.