519
ENDOSCOPIC VERSUS SURGICAL TREATMENT OF WEIGHT REGAIN FOLLOWING SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY
Date
May 19, 2024
Tracks
Related Products
MUCOSAL OXYGENATION SATURATION LEVELS FOLLOWING ENDOSCOPIC SLEEVE GASTROPLASTY
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gastroejejunostomy (EUS-GJ) has gained popularity in treating malignant gastric outlet obstruction (GOO). EUS-GJ has also been used to manage benign GOO with promising technical and clinical success…
PERSONALIZED THERAPY FOR THE TREATMENT OF WEIGHT REGAIN FOLLOWING ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS: AN ANALYSIS OF 900 CONSECUTIVE ENDOSCOPIC REVISION PROCEDURES
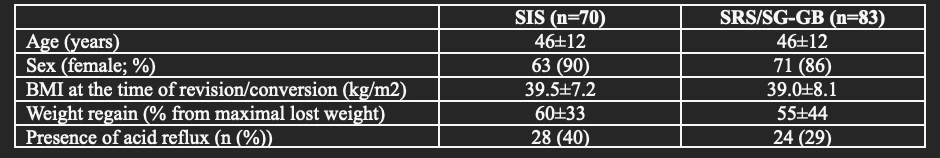
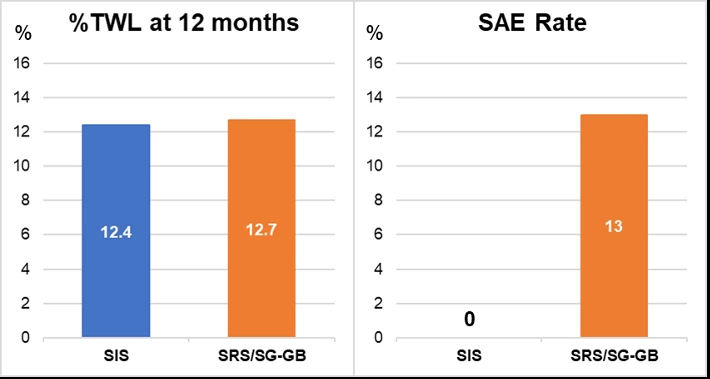
Background: Gastric sleeve stenosis (GSS) is an increasingly common adverse event following sleeve gastrectomy (SG) and thought to result from progressive rotation and/or scarring of the sleeve. Objective diagnostic criteria for this condition are lacking…
MULTICENTER PILOT RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL EVALUATING THE EFFICACY OF THE PRIMARY OBESITY SURGERY ENDOLUMINAL (POSE2.0) PROCEDURE IN OBESITY MANAGEMENT
BACKGROUND AND AIMS: The Primary Obesity Surgery Endoluminal 2.0 (POSE2.0) is an endoscopic gastric remodeling procedure that utilizes an incisionless operating platform (IOP, San Clemente, CA) to remodel the stomach and alter appetite (FIGURE 1)…
EFFECT OF ENDOSCOPIC GASTRIC REMODELING ON HISTOLOGIC METABOLIC DYSFUNCTION-ASSOCIATED STEATOHEPATITIS (MASH) AND LIVER FIBROSIS: A 12-MONTH PROSPECTIVE OBSERVATIONAL STUDY
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) is traditionally treated with lifestyle modification. Nevertheless, most patients are unable to achieve the 10% total weight loss (TWL) threshold required for fibrosis regression…